Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Read More >
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a common condition that affects the inner ankle and medial arch of the foot. In this article, we will cover the differential diagnosis between Posterior Tibial Tendonitis and other conditions of the foot and ankle.
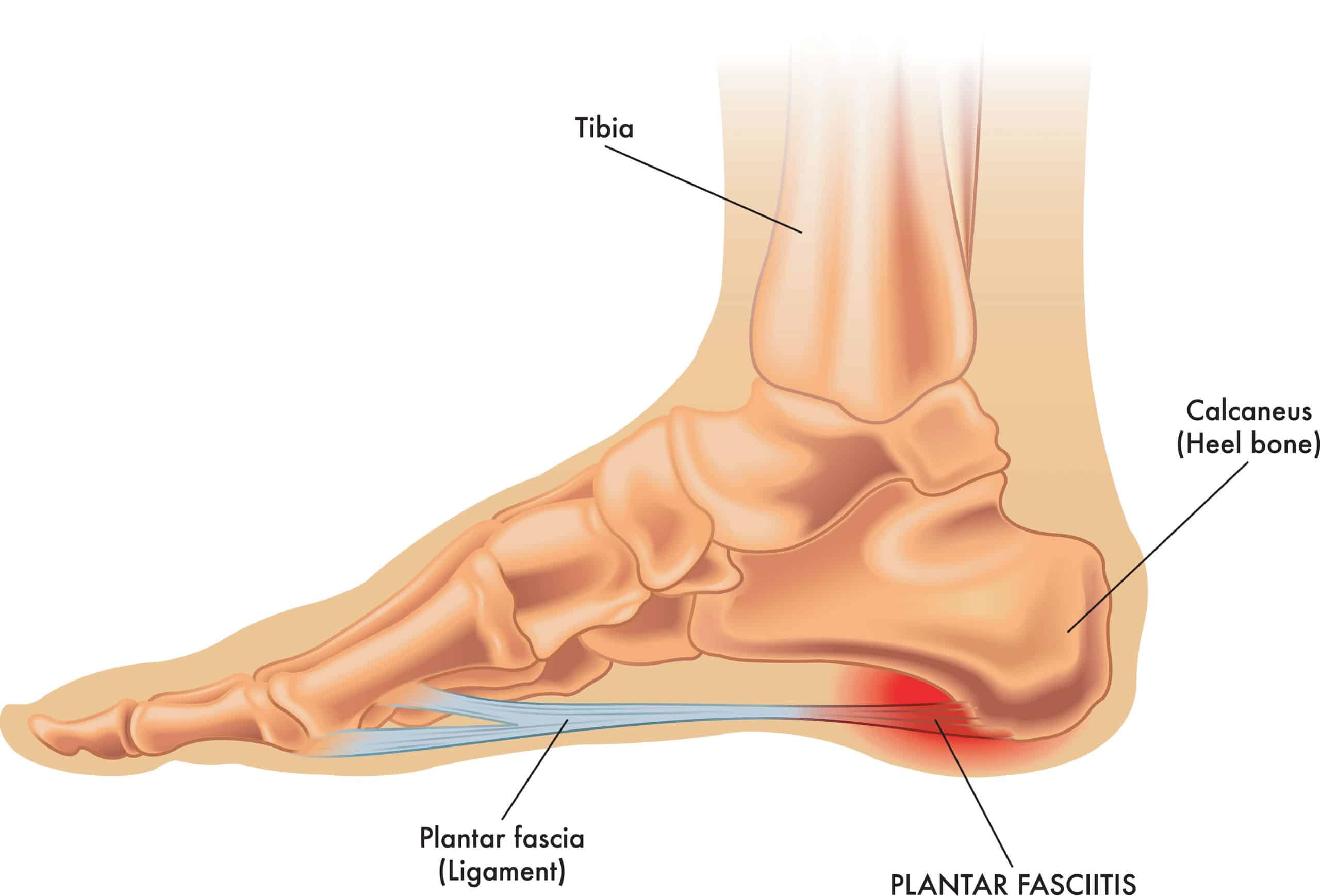
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis affects the posterior tibial tendon located on the inner side of the shin, reaching down and behind the medial malleolus and onto the medial arch of the foot.
In contrast, Plantar Fasciitis affects Plantar Fascia, located on the underside of the foot, attaching from the heel bone and spreading out like a fan across the underside of the foot and attaching to the forefoot.
The most common location of pain for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is along the inner ankle. However, there can be pain in the tendon’s attachment to the medial foot. When this occurs, it is referred to as enthesopathy rather than tendonitis.
Plantar Fasciitis is often most painful on its attachment to the inner heel bone, although there can be pain in the mid portion around the foot’s medial arch.
Both conditions are painful first thing in the morning, made worse with activity and improve when rested. A clinical examination can achieve a differential diagnosis alongside an ultrasound scan.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a condition of the Posterior tibial tendon where the pain is commonly located on the inner ankle and medial arch of the foot whereas Achilles Tendonitis is a condition affecting the long tendon at the back of the ankle.
Related Article: Symptoms and Treatment for Achilles Tendonitis

There can be some crossover between both of these injuries, especially if there has been a mechanism of injury, such as a medial ankle sprain.
This usually occurs when a sudden eversion of the ankle joint overstretches and tears the ligaments on the inner ankle. These ligaments are known as the deltoid ligaments. With a significant Deltoid ligament tear, the Posterior Tibial Tendon can also be overstretched, causing pain, inflammation, and tendonitis.
Secondly, a mild ankle sprain can lead to an antalgic gait pattern. This can overload other aspects of the foot and ankle, such as the Posterior Tibial Tendon, leading to Posterior Tibial Tendonitis. Finally, suppose there is no mechanism of injury. In that case, it is unlikely to be a sprained ankle, and there is a higher likelihood that your inner ankle pain results from Posterior Tibial Tendonitis.
Clinical evaluation of the deltoid ligaments will be sufficient to ascertain if there has been an injury to them, while pain along the tendon on palpation alongside pain on resisted inversion is indicative of possible Posterior Tibial Tendonitis.
Related Article: Best exercises for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
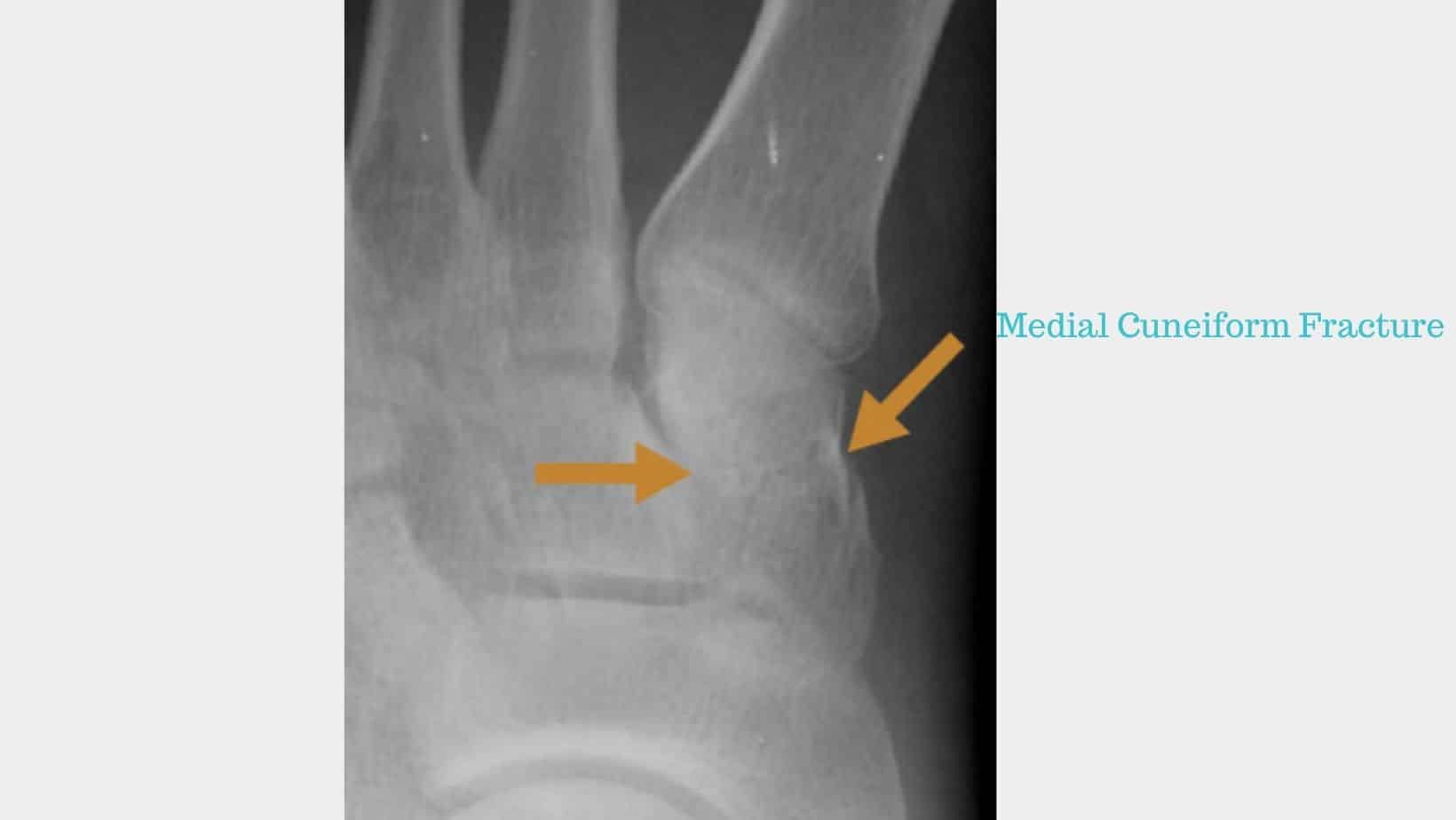
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis and stress fractures to the medial malleolus or the navicular bone can confuse.
Stress Fractures are often the result of a trauma such as a fall, awkward landing or something falling onto the bone. However, there can occur insidiously in people with low vitamin D levels, Osteopenia or Osteoporosis.
Taking this into account, some key differences are that Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is usually worse first thing in the morning, worse after activity but improves with rest. In contrast, a stress fracture is consistently painful with use.
Related Article: Causes of Medial Malleolus Pain
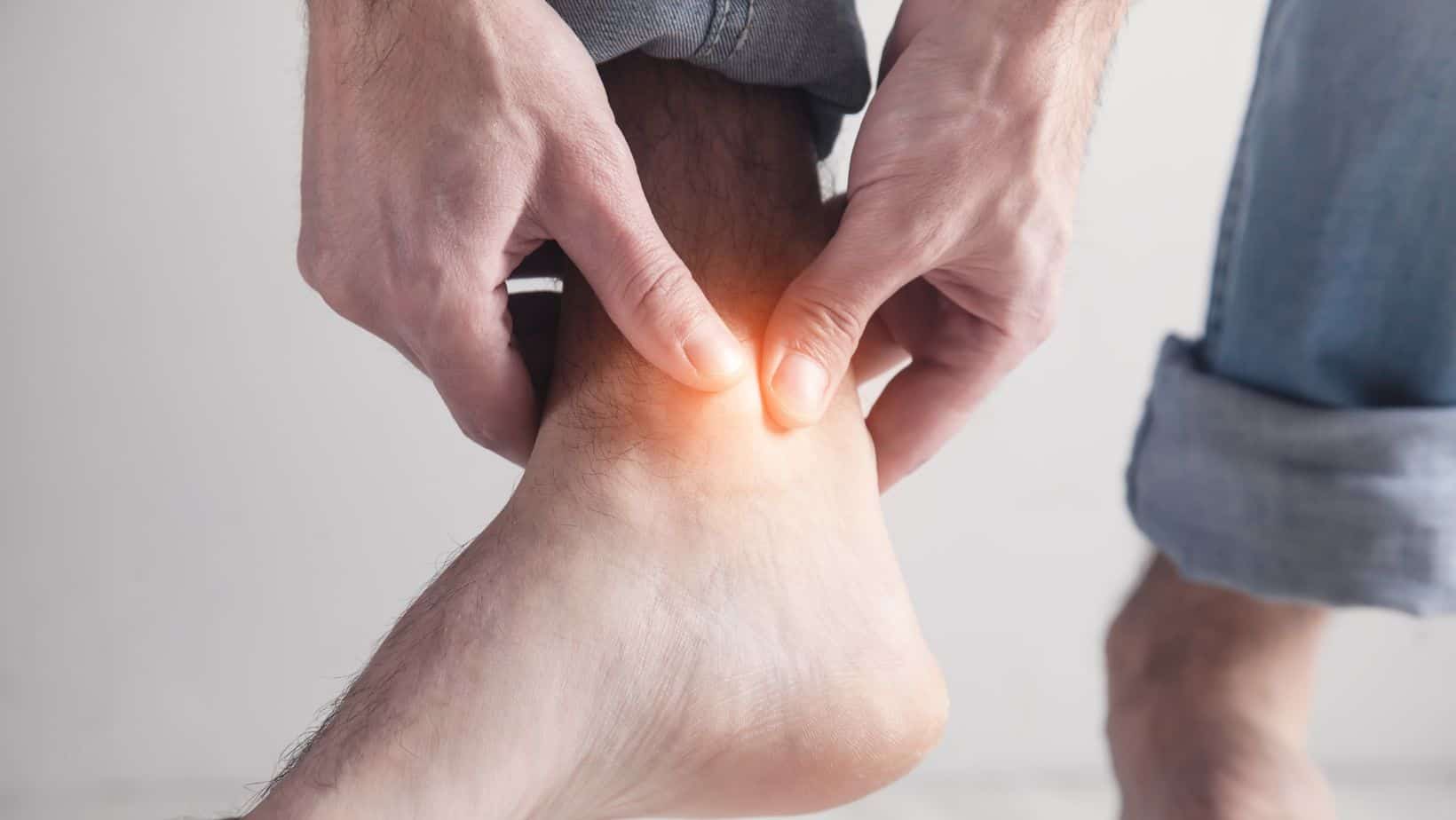
The Tarsal tunnel is a minor groove on the inner ankle that contains blood vessels, nerves and some fatty tissue, and this can become irritated through trauma or a biomechanical overload.
In that case, it often presents with inner ankle pain when walking, numbness or pins and needles on the inner aspect or top of the foot.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis can provide pain with use on the inner ankle. Along the medial arch of the foot during or after us, but unlike Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, it does not provide neurological symptoms.
Related Article: Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: Symptoms & Treatment