Achilles Tendinopathy: Achilles Tendon Pain
Read More >
The Achilles tendon sits at the back of the ankle connecting the calf muscle to the heel bone. The Achilles Tendon does not have a true synovial sheath; instead, it has a paratenon composed of flexible connective tissue that allows for tendon gliding with activity.
The function of the Achilles Paratenon is to protect the Achilles Tendon from surrounding structures and to reduce friction. The Paratenon has a very good blood supply, and when irritated, it can become painful and inflamed, leading to Achilles Paratenonitis. The paratenon is innervated by nerves from local cutaneous nerves—in particular, the sural nerve.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for Paratenonitis. It is sometimes referred to as Achilles Tenosynovitis.
Achilles Paratenonitis is often the result of an acute overload of the Achilles tendon or friction from a bony protuberance such as Haglund’s deformity. An overload results from a sudden increase in running or impact activities. Other causes can be poorly fitted footwear that causes friction of the paratenon.
Sharp constant pain along the entire Achilles Tendon is associated with Achilles Paratenonitis.
There can be audible crepitus when moving to flex the foot while it is common for swelling along the Achilles Tendon. The space between the tendon and the sheath fills with fluid to give it a swollen sausage-like appearance.
If you have any symptoms of Achilles Paratenonitis, it is recommended to see a Sports Medicine Doctor or Physical Therapist.
After a careful clinical interview followed by a clinical assessment, a swollen Achilles Tendon is normally observed alongside a positive Achilles tendon pinch test along the length of the tendon.
The differential diagnosis aims to rule out other common causes of pain in the area, such as:
A referral for imaging, such as an ultrasound scan or an MRI, are the most accurate form of imaging for Achilles Paratenonitis.
Treatment for Achilles Paratenonitis should be under the care of a Physical Therapist or Podiatrist.
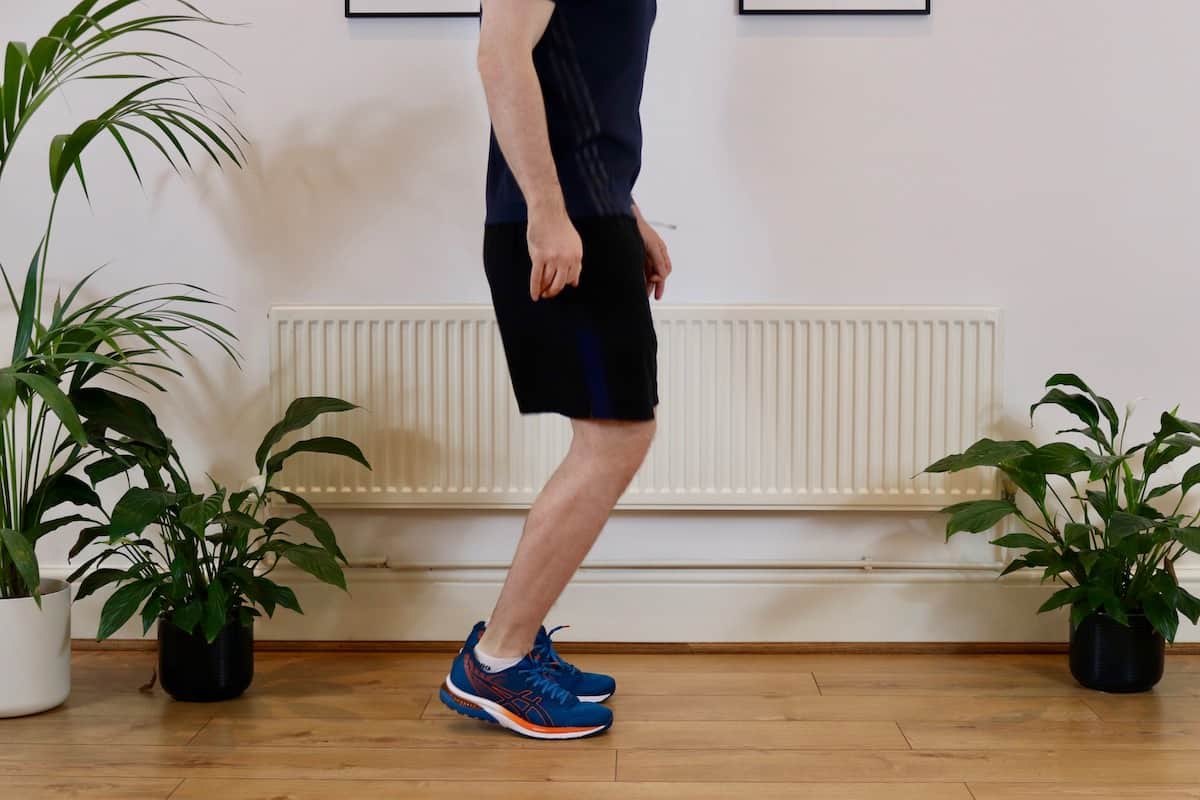
Offloading the area with non-steroidal anti-inflammatories can be highly effective in the acute stage. A heel raise in a shoe can shorten the Achilles Tendon, and Isometric strengthening exercises are helpful.
Offloading by dramatically reducing your step count or using a walker boot can benefit extremely irritable cases.
Shoes with a high heel drop, such as the Asics Gel-Kayano can offload the tendon.
Surgery is unnecessary for this condition as it normally settles quickly with the correct management.

This article is written by James McCormack, a Foot and Ankle Specialist who is an expert in treating mid-portion Achilles Paratenonitis.
This is not medical advice. We recommend a consultation with a medical professional such as James McCormack if you are experiencing any of the symptoms discussed in this article. James offers Online Physiotherapy Appointments weekly and face-to-face appointments in his London clinic.