Best Running Shoes For Shin Splints
Read More >
The ankle joint consists of the talus bone, tibia and fibula bones and they are surrounded by ligaments and tendons. A ligament attaches a bone to a bone while a tendon attaches a muscle to a bone and this article will cover all of the tendons that cross over the ankle including their attachment points and their action.
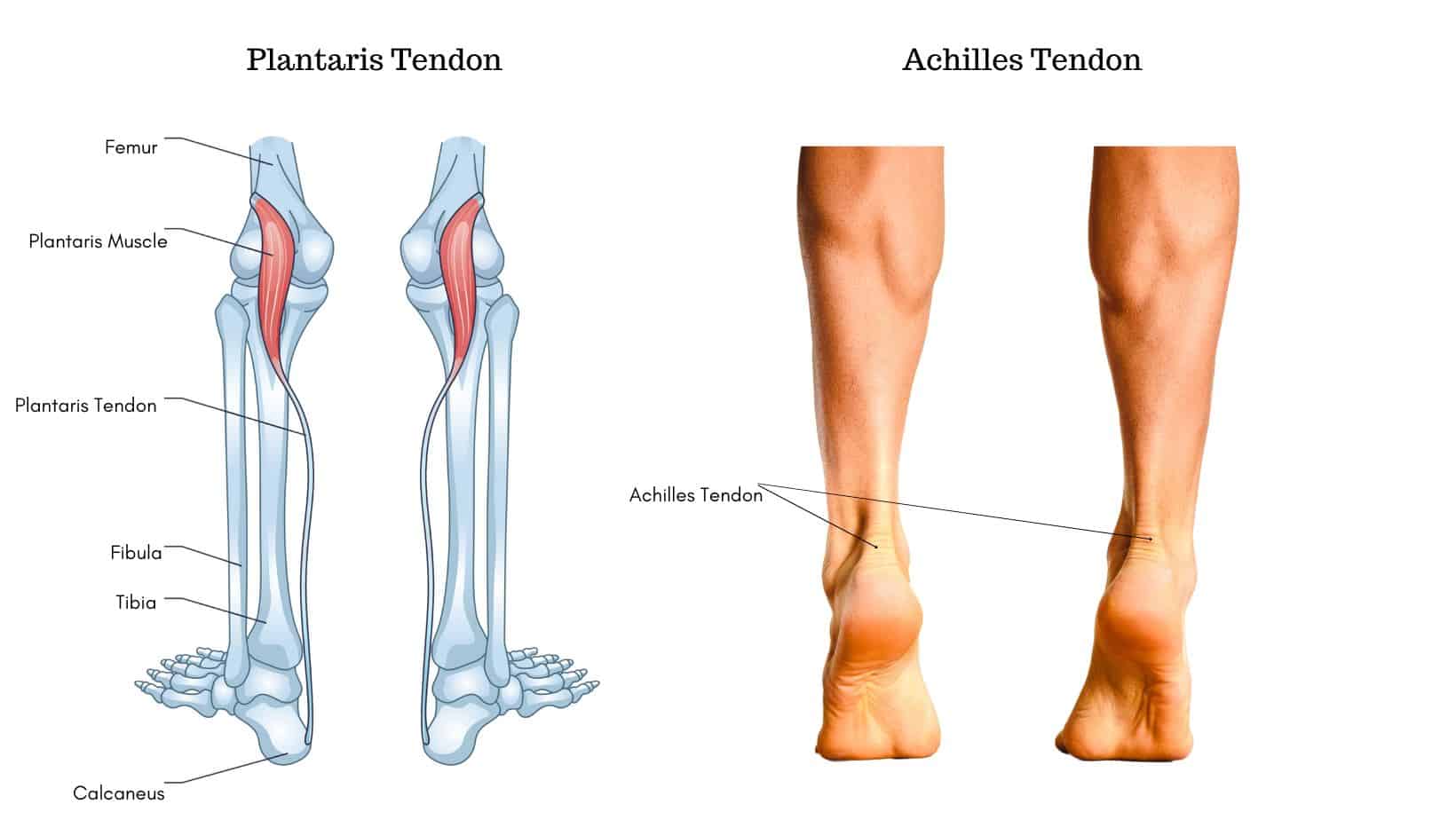
The Achilles Tendon attaches the calf muscles (Gastrocnemius and Soleus) to the heel bone (calcaneus). The primary function of the Achilles Tendon is to plantarflex the ankle and foot and it is both the largest and strongest tendon in the body.
The Plantaris Tendon is a thin spindle-shaped tendon that attaches the Plantaris Muscle to the heel bone, running alongside the inner aspect of the Achilles Tendon. The Plantaris Tendon’s primary function is to provide proprioception to the ankle.
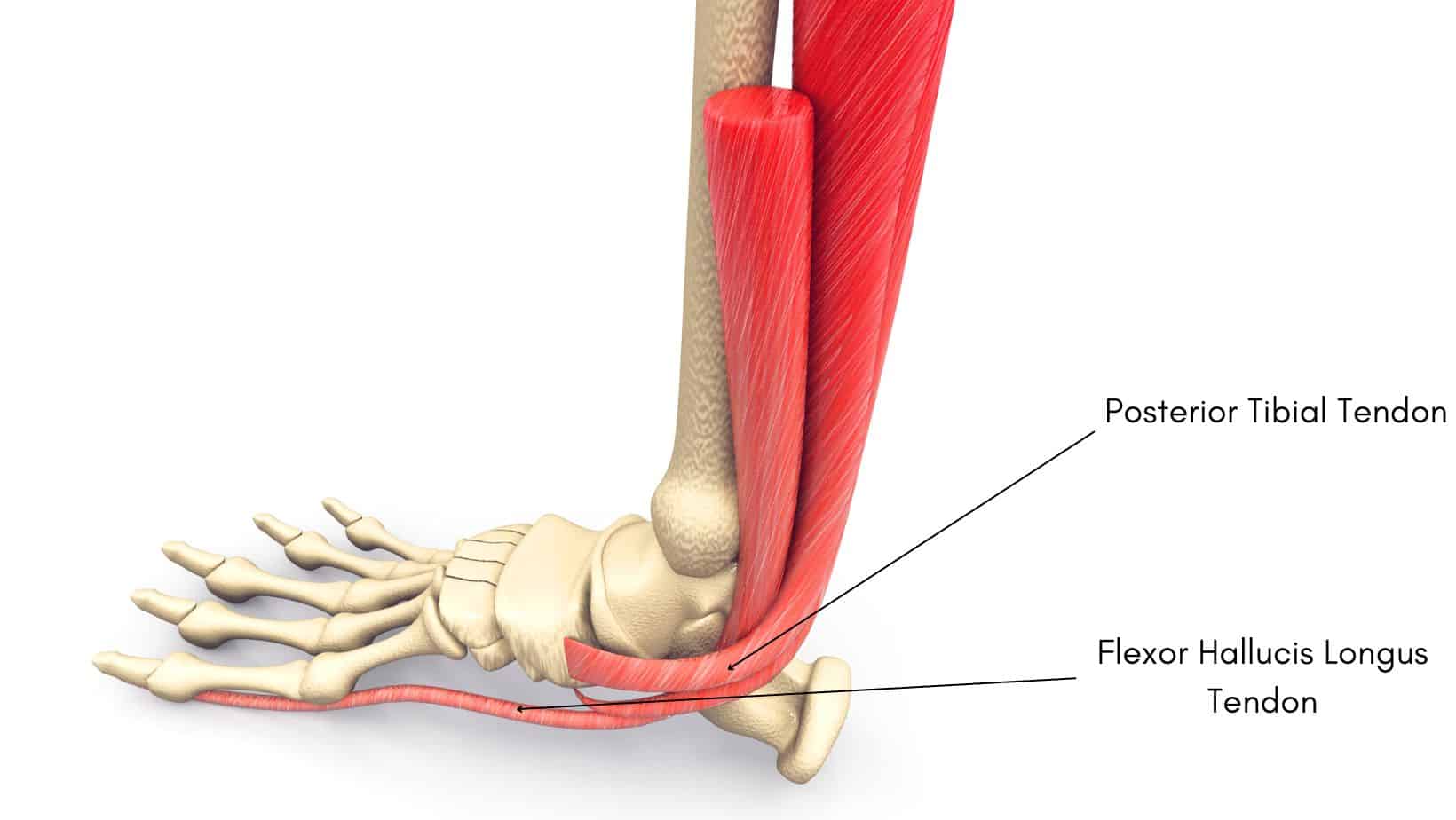
The Posterior Tibial Tendon runs along the inner aspect of the shin, around the medial malleolus (inner ankle bone) and attaches to multiple bones along the medial arch of the foot but primarily the navicular bone. The Posterior Tibial Tendon helps to invert the foot and plantarflex the foot and ankle while also acting as a key stabiliser of the foot and ankle.
The Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon attaches from the Flexor Hallucis Longus muscle to attach onto the plantar surface of the 1st hallux. The Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon aids plantarflexion of the ankle and flexes the big toe.
The Peroneal Longus tendon attaches the Peroneal Longus muscle to the lateral base of the first metatarsal and the medial cuneiform. The action of the Peroneal Longus tendon is eversion and assistance with plantarflexion of the foot.
The Peroneal Brevis tendon attaches the Peroneal Brevis muscle to the styloid process at the distal end of the 5th metatarsal. The action of the Peroneal Brevis tendon is to evert the foot and provide stability to the ankle.
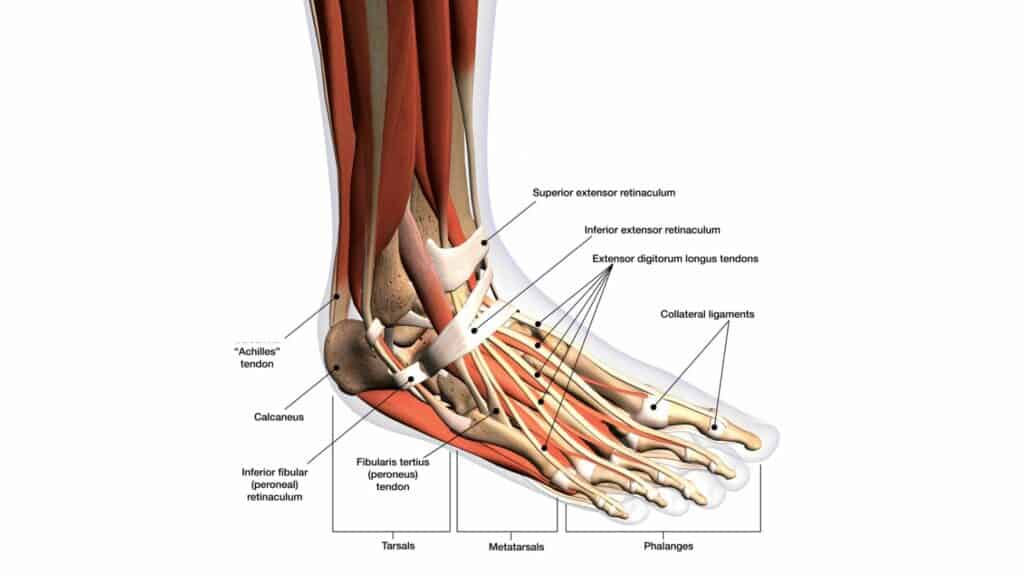
The Peroneal Tertius tendon attaches the Peroneal Tertius muscle to the dorsal surface of the 5th metatarsal. The action of the Peroneal Tertius tendon is to assist dorsiflexion and eversion.
The Extensor Digitorum Longus Tendon attaches the Extensor Digitorum Longus muscle, extends down and under the superior and inferior extensor retinaculum, splits into 4 segments and attaches to the 2-5th digits. The function of the Extensor Digitorum Longus Tendon is to extend the 2-5th digits and dorsiflexion of the ankle.
The Tibialis Anterior tendon attaches the Tibialis Anterior muscle to the undersurface of the first cuneiform bone, and the base of the first metatarsal bone. The function of the Tibialis Anterior tendon is dorsiflexion of the ankle, inversion and abduction of the foot while also assisting the stability the medial arch of the foot.
The Extensor hallucis longus tendon attaches the Extensor hallucis longus muscle to the base of the distal phalanx of the big toe. The function of the Extensor hallucis longus tendon is to extend the joints of the big toe and assist with inversion of the foot and dorsiflexion of the ankle.
This is not medical advice. We recommend a consultation with a medical professional such as James McCormack. He offers Online Physiotherapy Appointments for £45.
Related Articles:
Best Shoes for Walking – Heel Fat Pad Atrophy – Bruised Heel – Foot Pain Chart