Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
Read More >
Saphenous nerve entrapment is commonly referred to as Gonalgia Paresthetica. It is an uncommon but painful condition affecting the saphenous nerve. Chronic irritation to the nerve is caused by compressions and/or tension. Symptoms include pain and altered sensations such as hypersensitivity, numbness, or pins and needles along the dermatome of the nerve.
The dermatome of a nerve is the patch of skin that it corresponds to. For the saphenous nerve this is along the inside and front of the knee, and down the inner side of the shin and calf, reaching down to a portion of the arch of the foot.
Symptoms can be felt in this whole area or just a portion of it.
The most common entrapment or impingement site is where the nerve passes through the adductor canal, also known as Hunter’s canal. The nerve can also get compressed around the inside of the knee and the inner, lower leg.
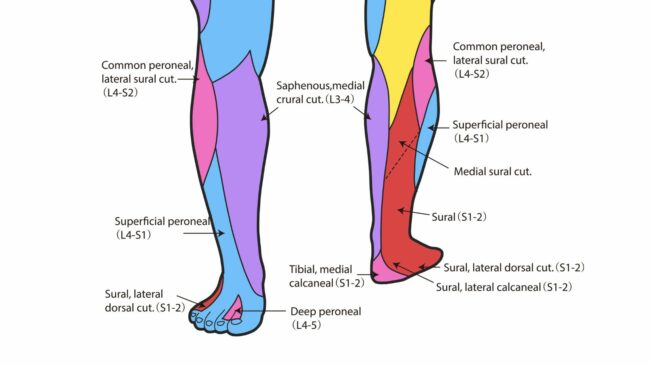
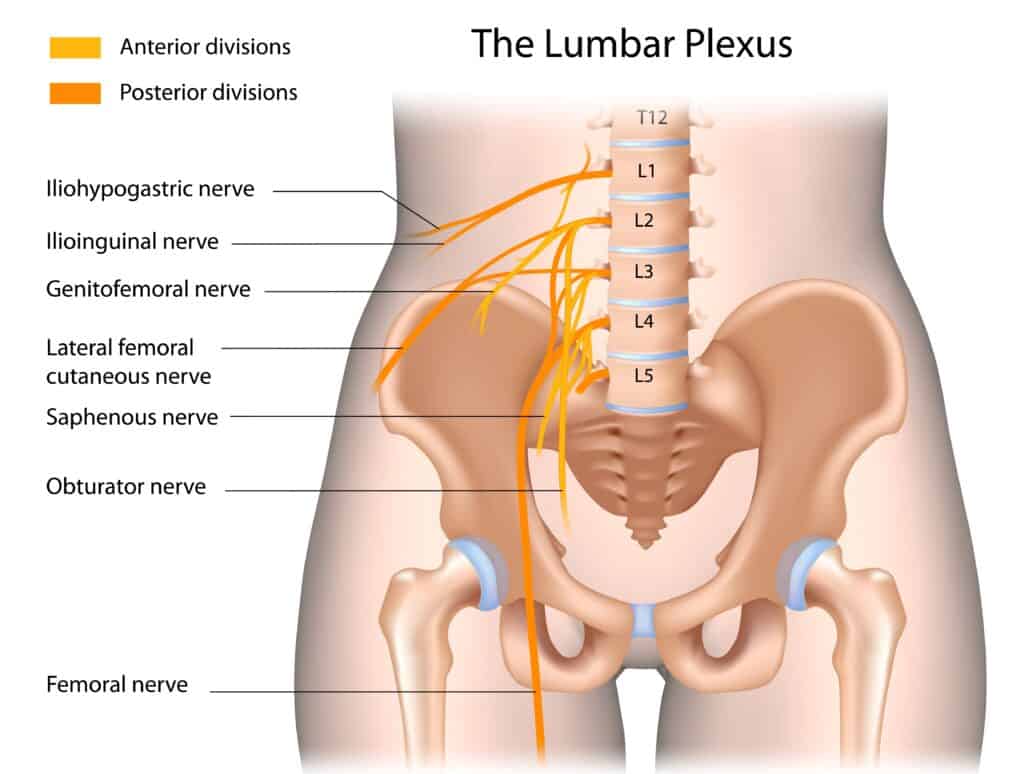
There are two major nerves in the leg: the sciatic nerve and the femoral nerve. The saphenous nerve is a branch of the femoral nerve. Both sciatic and femoral nerves leave the spinal cord at the lumbar plexus.
The saphenous nerve separates from the femoral nerve at the top of the thigh, where the femoral nerve splits in two. There is an anterior branch and a posterior branch. It is the posterior branch that becomes the saphenous nerve.
In most cases, the causes of entrapment are related to repetitive injury and chronic irritation. However, an injury to the nerve can occur related to trauma or surgery.
With the surgical route taken for procedures such as total knee replacement or ACL repairs, the saphenous nerve is vulnerable to damage. It is a recorded risk for both surgeries as well as others.
The necessary use of clips during surgery can cause the nerve to be pinched. This compression can result in nerve damage in the knee. Additionally, a cut to the nerve may cause more severe damage.
The saphenous nerve only has a sensory function. The saphenous nerve enables you to feel touch, pain and temperature. It also enables you to know where your leg is and what position it is in.
The saphenous nerve has no motor function, which means it does not stimulate muscles to contract.
A saphenous nerve entrapment test commonly used is the Tinel test. It is a repeated percussion or tapping applied to a superficial points of the nerve.
A nerve tension test can also be used. This moves the limb in a sequential way to tension the nerve.
Both tests can indicate whether the nerve is involved if they reproduce pain and other symptoms.
Palpation can also give information about the location of the injury. However, as a large portion of the nerve lies deep in the leg under the muscle it can be less accurate.
To confirm the diagnosis, a nerve conduction study can be performed, and radiology such as MRI and ultrasound can be used.
Saphenous nerve pain treatment should be directed by a medical professional, such as a physical therapist. This is a relatively uncommon condition. Therefore, finding a therapist with experience treating this specific issue is important.
Treatments to aid recovery can include rest, massage and exercises. Hands-on physical therapy may also mobilise the joints of the lower back, hip, knee and ankle. In many cases, this will be an effective treatment. However, in some cases of persistent pain and other symptoms, these conservative treatments are not adequate, and injections or surgery may be necessary.
The conservative management of saphenous nerve pain includes hands-on physical therapy such as massage to the muscles and mobilisation to the joints of the lower back, hip, knee and ankle.
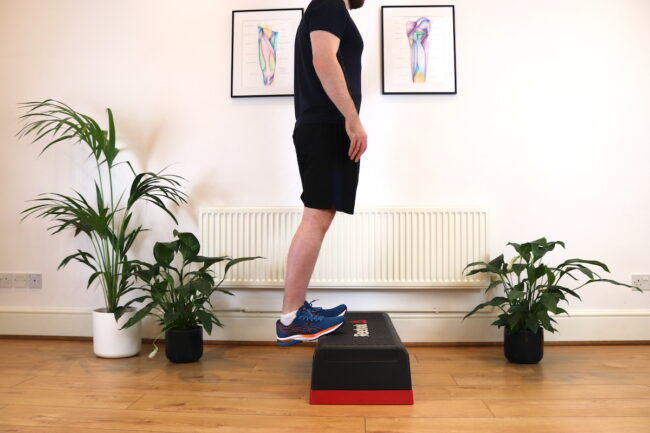
Exercises for saphenous nerve entrapment pain include mobility of the joints and muscles along the course of the nerve. They include lower back mobility, glute, quadriceps, and calf muscle stretches.
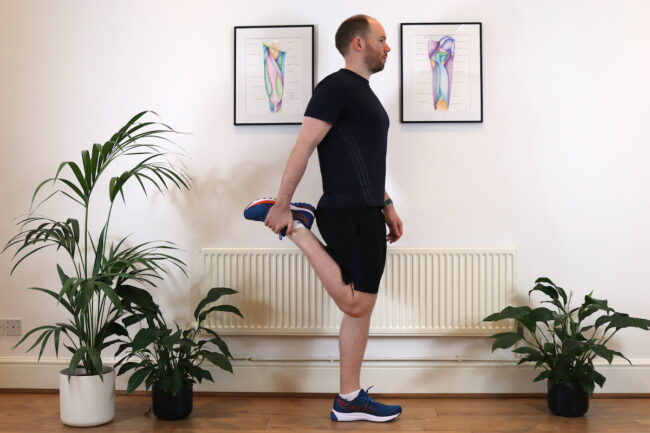
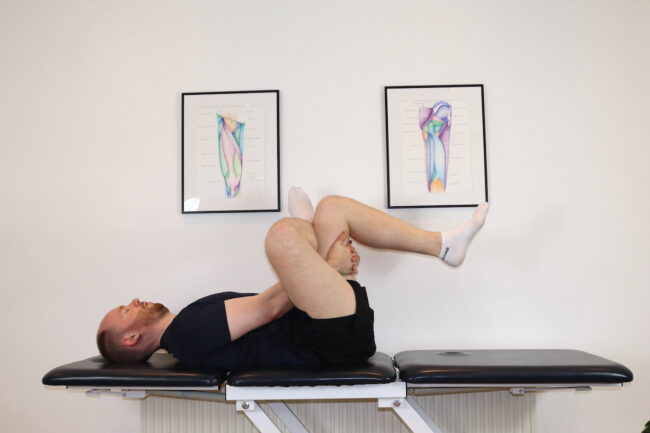

A specific exercise can be done to release the nerve called a nerve glide. Once the course of the nerve has been freed of any stiffness of joints and tightness of muscles, the nerve itself can be mobilised.
Neurodynamic exercises move the nerve along its course by drawing it in one direction followed by the opposite. However, there is mixed evidence for how effective they are.
For the saphenous nerve, this involves extending the hip, abducting the hip, and everting the foot. Then, you should ease out of this position to allow the nerve to glide back. This can be done by standing in a similar position to a yoga Warrior Pose. This can be repeated 10-20x, allowing the nerve will glide back between each repeat. This can be a very effective way to reduce pain.

Surgery, like for most injuries, is a last resort. It should be reserved only for when other treatment options have been tried and not been ineffective.
A saphenous nerve block can be an effective treatment if other treatments have not. They are carried out under ultrasound guidance to ensure the correct location and administration of the medication. There are two forms of nerve block: surgically and non-surgical.
Epidural anaesthetic or spinal injections of analgesia are injections into the space around the spinal cord.
A peripheral nerve block is an injection to the nerve more local to where the injury is that is causing the pain or symptoms.
Rhizotomy is the surgical destruction of the specific nerve root of the nerve at the spinal cord.
Neurectomy is the surgical destruction of the peripheral nerve causing the symptoms.
This article is written by James McCormack, a Lower Limb Specialist who is an expert in treating Knee Pain, including Saphenous Nerve Pain.
This is not medical advice. We recommend a consultation with a medical professional such as James McCormack if you are experiencing any of the symptoms discussed in this article. James offers Online Physiotherapy Appointments weekly and face-to-face appointments in his London clinic.