Read More >
- Anterior Ankle Impingement - July 24, 2022
- Tarsal Coalition - October 12, 2022
- Sural Nerve Pain - October 3, 2022
What is Extensor Tendonitis of the Foot?
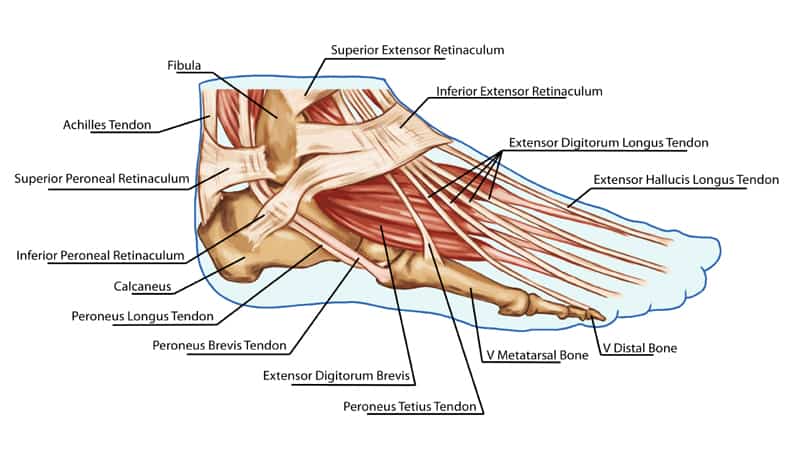
The Extensor tendons sit on the top of the foot and their function involves lifting the foot and toes. The main extensors of the foot are the Extensor Hallucis Longus, Extensor Hallucis Brevis, Extensor Digitorum Longus, and Tibialis Anterior. If these tendons become overloaded, it can cause pain and inflammation on the top of the foot, resulting in Extensor Tendonitis.
Symptoms of Foot Extensor Tendonitis
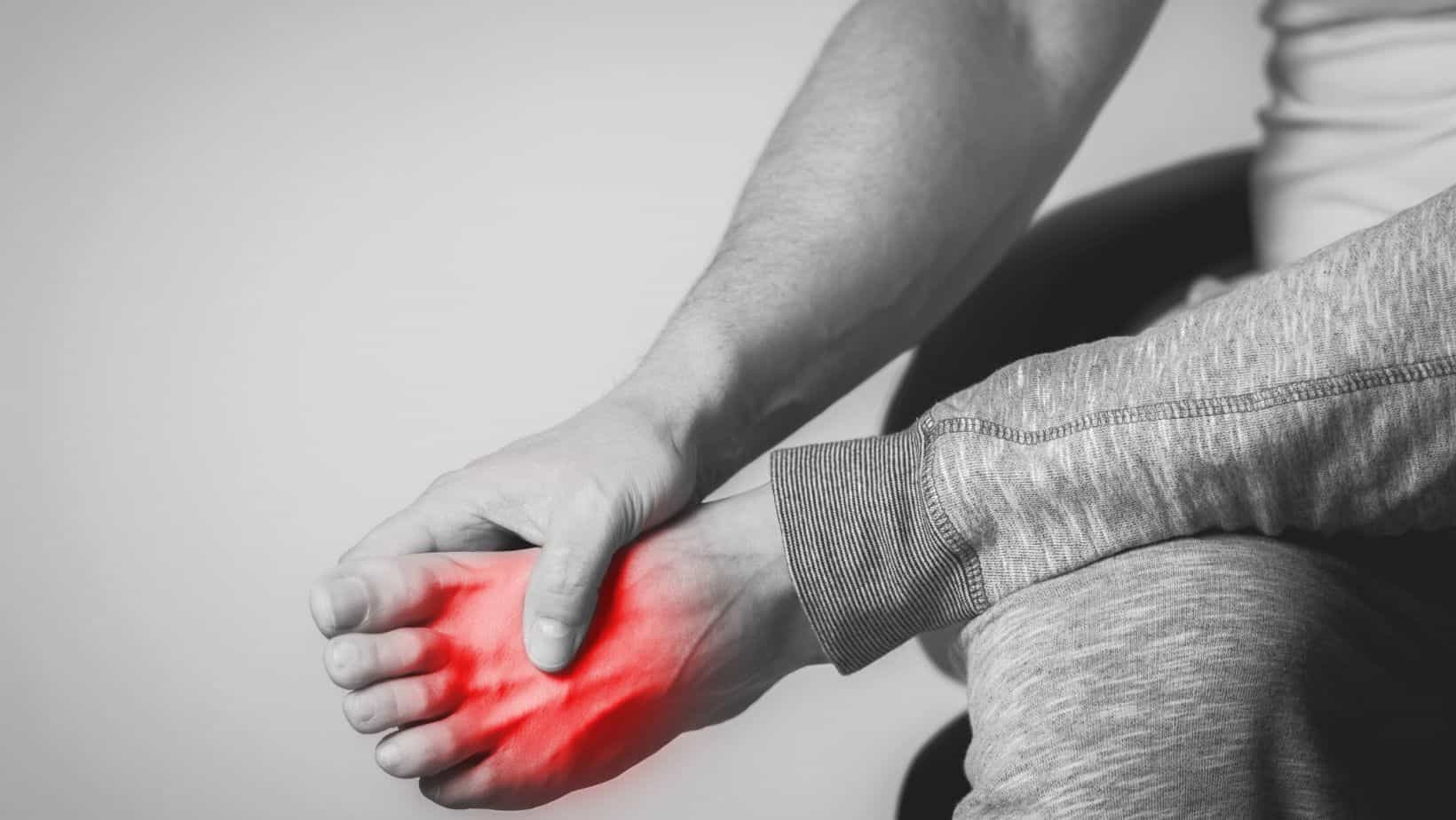
The symptoms of Extensor Tendonitis include pain and discomfort on the top of the foot that is exacerbated by lifting the foot, walking uphill or running. In most cases, symptoms are gradual in onset, worse in the morning and at the start of exercise but improve as they warm up.
Symptoms are aggravated by wearing tight-fitting shoes, especially tightly laced shoes. Heavier shoes, such as heavy boots or fashion shoes with thick soles, can irritate symptoms further.
Causes of Extensor Foot Tendonitis
Extensor Tendonitis of the foot is caused by an overload or overuse of the foot. Typical examples would be a sudden increase in walking uphill as the extensors have to work hard to lift the foot.
Biomechanical foot issues such as a flat foot or poor control of pronation moments when walking can cause Extensor Tendonitis of the foot as the extensor muscles can be overworked.
Diagnosis of Extensor Tendonitis of the Foot
A clinical examination by a Physical Therapist or a Podiatrist can identify the presence of extensor tendonitis based on a patient’s symptoms and a physical examination.
If the clinician would like to rule out other causes of top-of-the-foot pain, they might refer you Ultrasound Scan or an MRI to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for Extensor Tendonitis of the Foot
Physical Therapy is the best treatment for Foot Extensor Tendonitis, which involves a Physical Assessment of flexibility, mobility and strength. A gait analysis may also be required to assess the best shoes for the condition or the necessity for insoles.
A thorough rehabilitation programme consisting of strengthening and stretching exercises can be created after these examinations and combined with anti-inflammatories and exercise modification; this strategy is highly effective at healing Extensor Tendonitis.
In stubborn cases, shockwave therapy may be recommended, while steroid injections are rarely recommended for tendon-related issues.
Physiotherapy with James McCormack
This is not medical advice. We recommend a consultation with a medical professional such as James McCormack. He offers Online Physiotherapy Appointments for £45.
Related Article: Anterior Tibial Tendonitis: Symptoms & Treatment
